Every one of you might have come across orifice plates. The primary sensing element we use most widely for measuring the flow of fluids.
Very simple and with good accuracy, orifice meters are very famous in every industry for flow measurement.
How does an orifice flow meter work?
Orifice flow meters are the inline types of flow meters i.e. They are installed inside the pipe. The orifice plate is the primary sensing element. This element creates a differential pressure across itself.
The upstream pressure is high compared to the downstream pressure. We take 2 tapings, one from upstream and 1 from downstream, and give them to a differential pressure transmitter.
Now you might know that the flow flowing through the line is proportional to the square root of the differential pressure we get from the differential pressure transmitter.
We get a differential pressure from the differential pressure transmitter and this differential pressure is converted to flow using the mentioned square root proportionality (ready option available for selection whether the function is linear or square root).
The square root should be in 1 place only. Either in the field i.e. in transmitter or in PLC/DCS. Implementing square root on both sides will give wrong readings.
The place in the orifice plate where we get maximum velocity is termed a Vena-Contract point. The pressure here is very low.
The orifice plate is always designed considering an important term or factor called the Beta Ratio.
What is a Beta Ratio?
The beta ratio is the ratio of the orifice plate’s internal diameter divided by the pipe’s bore
Beta Ratio = orifice internal diameter / pipe bore
The value of the beta ratio for orifice is always between 0.3 and 0.75
If you want to know the fundamentals of the Beta ratio and why its acceptable value is between 0.3 to 0.75 then I recommend this video from my friend’s youtube channel.
What are the different types of orifice plates?
1. Concentric type Orifice Plate
The concentric orifice plate is the simplest form of the orifice plate. We are using a concentric orifice for measuring the flow of clean service fluids or gases.
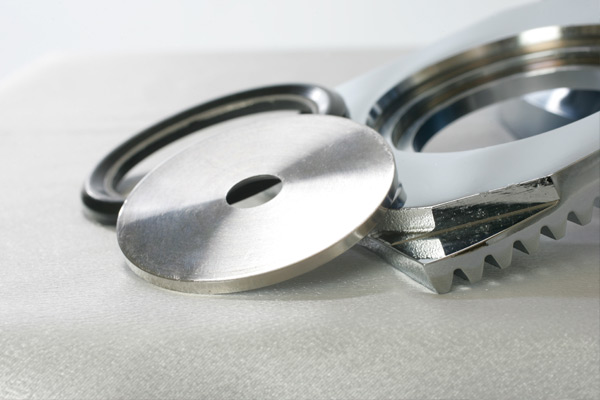

The plate of this type of orifice has a simple bore on the inlet and a beveled structure on the outlet.
This structure is designed to recover pressure loss. We use concentric type orifice plates for fluids having Reynolds numbers between 80 to 1500.
2. Eccentric type Orifice Plate
Eccentric type orifice plates are the same as other orifices but with a slightly different location of the bore. The bore of the eccentric plate is either located on top of the plate or at the bottom of the plate.

For gaseous services, as the gas travels in the top location of the pipe, the bore is in the top location of the plate for easy travel of gases.
While for liquids, the bore is in the bottom location for easy travel of liquids. We use eccentric type orifice plates for fluids having Reynolds number between 3000 to 12000.
3. Quadrant Edge Orifice Plate
The quadrant edge orifice plate has a different structure in the bore. This orifice is mainly designed for heavy viscous fluids.
There are 2 bores in the orifice plate that are in counterbore condition (two bores with the same center but different diameters).
This orifice is mainly used in heavy crudes, viscous syrups, and other heavy chemical flow measurements. We use quadrant edge type orifice plates for fluids having Reynolds numbers between 1500 to 9000.
4. Segmental type orifice plate
The most different type of orifice in terms of design is the segmental type orifice plate. This orifice does not have a full bore. Instead, as the name suggests, this orifice plate has a segment of the bore.

This segment is usually at bottom of the plate and is used for the heaviest fluid flow measurement. We use eccentric type orifice plates for fluids having Reynolds numbers between 5000 to 20000.
Why does an orifice have a vent and drain hole?
As we know, we use an orifice plate for measuring the flow of liquids and gases.
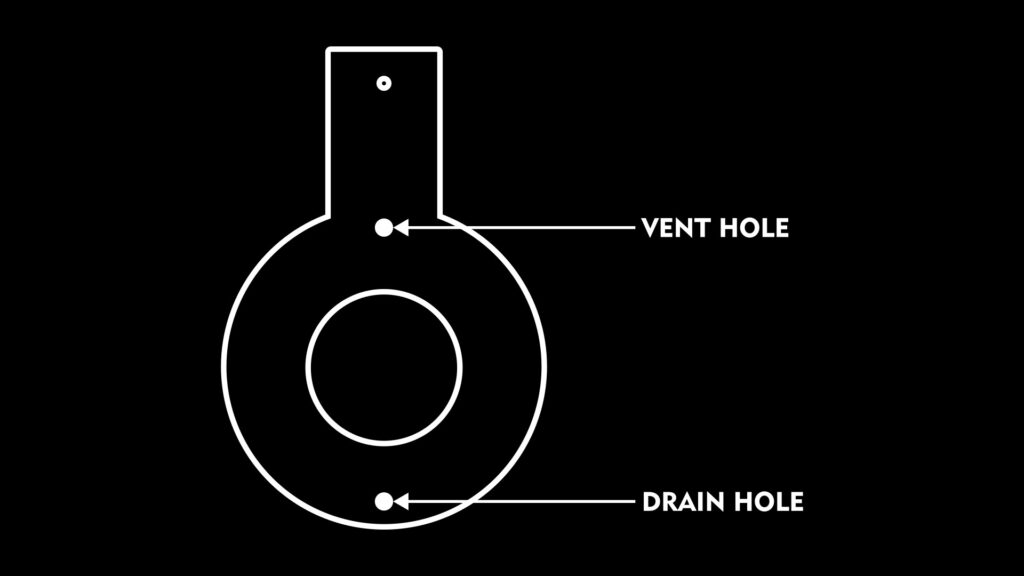
Suppose we are measuring the flow of water and what if vapors form? Yes, they will get built up on the top side and create problems for orifice plate differential pressure.
Now think of another case where we are using steam. Here condensed steam will build up in the bottom and create problems in differential pressure.
For eliminating this problem of buildup, a hole in the top is usually provided in liquids and a hole in the bottom is provided in gases.
Types of Orifices tapping
if you are wondering how different pressure transmitters are connected across orifice plates.
I will explain different types of orifices tapping that are used for connecting two legs of a Differential pressure transmitter, one is for HP tapping from upstream and another for LP tapping from Down Stream.
To understand different types of orifices tapping I will recommend this YouTube video from my friend Asad shaikh.
For ease of maintenance nowadays orifice plate is mounted through the orifice plate fittings assembly shown below image.
By using orifice plate fitting assembly Orifice plate is directly acceptable by maintenance personnel without opening whole pipe flanges and performing mechanical work-intensive tasks.
It will help companies to reduce the maintenance costs of the Orifice plates and save time.
and as you see below the image, multiple taping points are given across the orifice plate for connecting DPT.
There are two types of orifice fitting assembly available in the market as shown below.
- Single Chamber Orifice Fittings
- Dual Chamber Orifice Fittings
1. Single Chamber Orifice Fittings
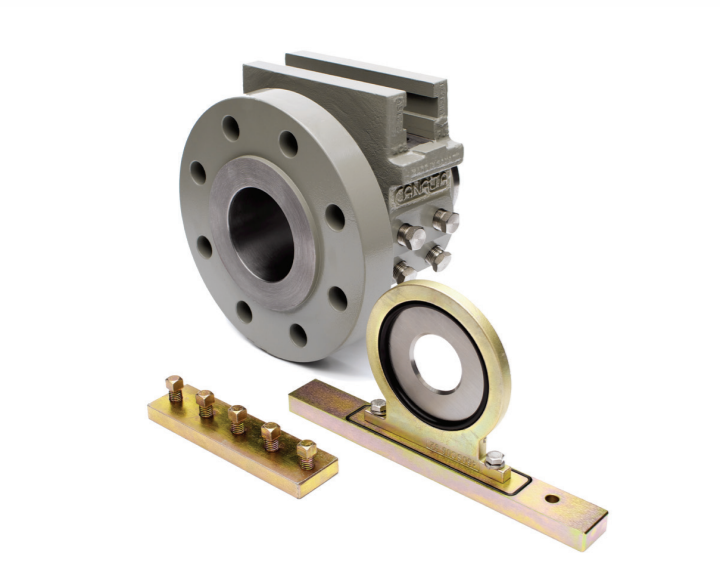

2. Dual Chamber Orifice Fittings
End Note
I hope now you have an idea about the Orifice plate and How it is actually mounted in the field. This article is mostly based on how the Orifice plate is used to create differential pressure.
If you like this post you can also like my previous article on Specifications that need to be considered before selecting DCS
And you can also follow our LinkedIn group which is specially made for sharing information related to Industrial Automation and Instrumentation.