🧠 Introduction
Selecting the right pressure gauge range is a fundamental step in instrumentation engineering. A properly sized gauge ensures accurate readings, protects the instrument from overload, and increases operational safety.
This updated guide presents a simple and effective method to choose the correct range for any application.
⚠️ Why Is Pressure Gauge Range Selection Important?

Incorrect range selection can:
- Cause damage to the gauge during overpressure events.
- Reduce readability and accuracy.
- Compromise safety and process control.
Right range selection ensures:
- ✅ Gauge longevity and performance.
- 📊 Reliable readings under steady and dynamic conditions.
- 👨🔧 Maintenance efficiency and fewer replacements.
⭐ Understanding Pressure Gauge Range
A pressure gauge is designed to operate safely within its full-scale (FS) range. If the gauge operates too close to its maximum limit, the Bourdon tube can deform, resulting in permanent damage and inaccurate readings. If the range is too high, the operator cannot read small pressure changes.
Your goal is to find a balance between accuracy and durability.
⭐ The Recommended Engineering Rule (20–80%)
Industry standards recommend:
- Normal operating pressure should be between 20% and 80% of the full-scale range.
This ensures:
- Good pointer resolution
- Reduced mechanical stress
- Longer instrument life
⭐ How to Apply the 20–80% Rule
The selection method is:
- Identify normal and maximum operating pressures
- Calculate an acceptable FS range using the rule:
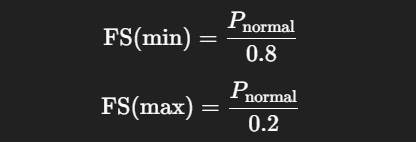
- Choose the nearest higher standard range within this band
- Ensure the gauge can safely withstand design pressure
- Finalize based on process conditions (pulsation, corrosive fluid, temperature)
⭐ Standard Pressure Gauge Ranges
Common Bourdon tube gauge ranges include:
- 0–1 bar
- 0–1.6 bar
- 0–2.5 bar
- 0–4 bar
- 0–6 bar
- 0–10 bar
- 0–16 bar
- 0–25 bar
- 0–40 bar
- 0–60 bar
You should always select the next higher available range. And pls refer ASME B40 100 for standard pressure gauge range.
⭐ Practical Example
Given:
- Normal Pressure = 5 bar
- Maximum Pressure = 7 bar
Apply 20–80% Rule
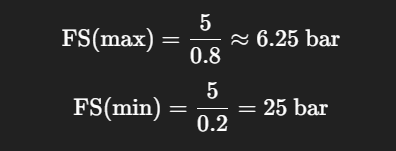
Acceptable FS range is between 6.25 bar and 25 bar.
Choose Standard Range
The closest available range above this value is:
→ 0–10 bar
or
→ 0–16 bar
Final Selection:
If the operating condition is stable → 0–10 bar
If there is pulsation, vibration, or pump discharge → 0–16 bar
⭐ Final Summary
To select the best pressure gauge range:
- Keep normal pressure between 20–80% of FS
- Use the next higher standard range
- Ensure gauge is safe for design pressure
- Confirm suitability for process conditions
✅ Conclusion
Pressure gauge range selection isn’t just about matching a number—it’s about ensuring safety, accuracy, and system longevity. By applying these simple principles:
- Know your system’s behavior.
- Choose the proper range.
- Always add margin for reliability.
Pls also refer specific client project requirements for pressure gauge range selection.
if you want to write an article on the website, please contact us by this mail id: contact@worldofinstrumentation.com
If you like this article, and if you want to know about hookup drawing. Check out my previous article.
And you can also follow our LinkedIn group which is specially made for sharing information related to Industrial Automation and Instrumentation.


