
Introduction:
“Real industrial productivity relies on the good maintenance of the equipment.”
Modern industries face many problems due to increased maintenance costs and unexpected downtimes.
Though we have industrial automation (SCADA) and condition-based maintenance, this problem remains inevitable. Thanks to artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) transforming most businesses.
Especially the role of AI-based maintenance in the manufacturing sector is enormous. it helps to identify equipment failure in much more advance than human intelligence.
From cost cut-off to zero downtimes. From safety operations to improved maintenance, AI has much to offer.
Now, let us see how AI-based predictive maintenance works in the manufacturing sector. Before going into much detail about predictive maintenance, let’s go through some basics.
What is Plant Maintenance?
Maintenance is the most important term used in the manufacturing and production sectors. The way you maintain your equipment ensures your plant is in good working condition.
This involves regular monitoring and replacement of damaged parts in a minimal time. So that we can meet our production deadlines without much downtime and interruptions.
In general, Plant maintenance has 5 types:
- Reactive Maintenance
- Time-based maintenance
- Preventive Maintenance
- Condition-based Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance
Reactive Maintenance: This maintenance is only performed when equipment malfunctions.
For short-term purposes, this maintenance is fine but not for the long term. Because this type of maintenance reduces productivity.
Time-based maintenance: Depending on our needs, this maintenance is done on a regular basis. which might be daily, weekly, or monthly.
This requires proper scheduling and planning. This type of maintenance is also known as planned maintenance.
Preventive Maintenance: This involves the repair of faulty equipment in a minimal way.
So that one can avoid the damage on a large scale and improve productivity. Preplanning and monitoring play a major role here in this maintenance.
Condition-based Maintenance: Uses sensors to check conditions and changes in asset data. This uses the KPI (key performance indicators) of equipment to analyze.
So that you can schedule your maintenance based on its performance. In the long run, this optimizes total efficiency and is cost-effective.
Predictive Maintenance (PdM): Like condition monitoring, sensors analyze the data of equipment.
But the key difference we can identify is asset failure in much advance. so that you can plan maintenance instead of relying on KPI changes in the equipment. This saves time and money.
Among the above maintenance techniques, the predictive maintenance method provides accurate predictions. So let us get into the PdM in detail being in the world of industrial revolution 4.0.
Need For Predictive Maintenance:
The main aim of PdM is to alert the equipment’s health much before its malfunctioning stage. Below are the 4 important points because you need PdM:
- To analyze the key factors causing equipment damage
- Predicting the downtime based on machine interruptions
- Offers scheduled maintenance ahead of regular repairs
- Early identification of hazards and safety issues.
How does PdM work?
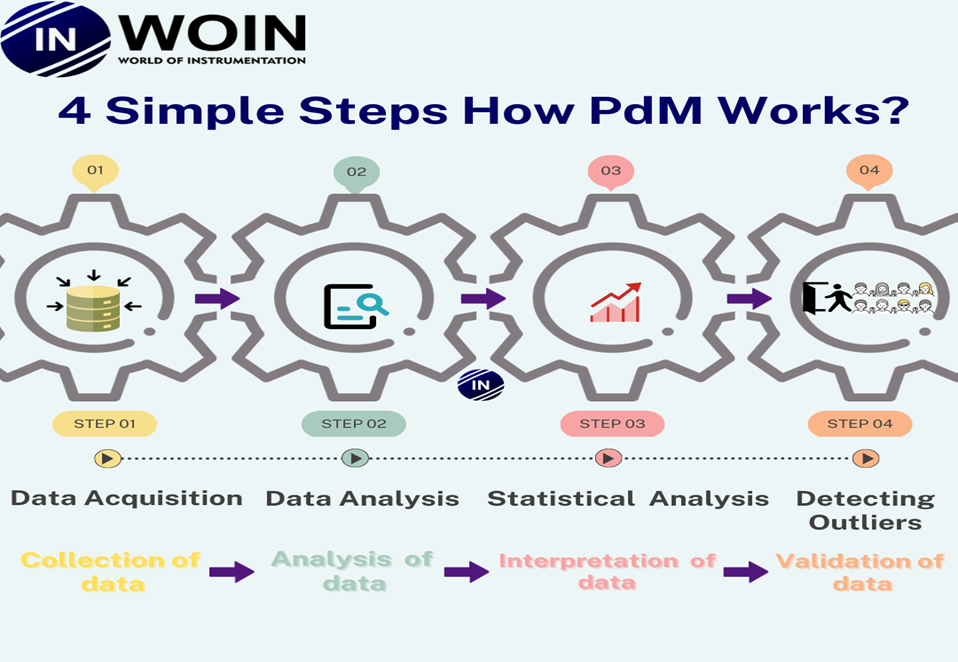
Predictive maintenance uses statistics, analytics, and other machine-learning algorithms for prediction. The below image shows the workflow of PdM as follows:
1. Data acquisition:
The first step of predictive maintenance involves data collection using sensors. Sensors embedded across the equipment check every parameter.
Which can be set based on our requirements like speed, temperature, and so on. This process of data collection and segregation from various resources is called data mining. This differs from business to business (B2B).
Now the collected data is been integrated into 2 forms as follows:
- Human Monitoring
- CMMS
Human Monitoring:
Whenever the sensor finds a fault, it alerts the administrator for further action.
This requires humans, where a maintenance person performs decisions either manually (or) remotely. Depending on the industry and the need, this activity differs!
CMMS
The term CMMS stands for a computerized maintenance management system. Which monitors the assets’ data and provides scheduled maintenance reports.
In a nutshell, CMMS is a DB (Database) that integrates sensor data using the internet. And the so-called Internet of things.
This connects two or more software devices to exchange data without any duplicity.
2. Data Analysis:
After the data collection, it undergoes further analysis for structuring. Because the collected data will be in huge numbers.
So, it will be in an unstructured manner. So, this process helps us to identify the particular data of our choice.
3. Statistical Analysis:
The process of collecting and interpreting numerical data is called data analysis. Thich involves the classification of data using patterns, graphs, models, and other KPIs’.
4. Detecting Outliers:
Datasets that deviate from other datasets are known as outliers. Proper validation and checking allow checking these outliers.
For instance, if 5 people are walking from left to right, but one walks from right to left. Then that one person is an outlier.
Once we identify the outliers, now it’s time to complete your model. This is called predictive modeling. Now monitoring the predictive model is essential before deploying it for future analysis.
Algorithms in PdM
- Simple linear regression
- Neural Network
- Decision Trees
- KNN.
Hope the above information might have given some knowledge that how the PdM works! Now it’s time to see how PdM plays ahead of traditional SCADA and DCS in industrial automation.
Important points to consider while implementing predictive maintenance?
Nowadays predictive analysis has created big hype across the world. Especially in the industrial sector to move towards predictive maintenance.
Heading toward technology is fine but one should look before leaping. So kindly take care of the below points:
- Check whether you have updated sensors to collect and transfer data with the IOT cloud.
- Is your control system capable of integrating all your needs with PdM software?
- Will PdM eases your needs of the management?
- Installation cost and does it Fit under your budget?
What are IoT Sensors? How does it differ from normal sensors?
The term IoT stands for Internet of things. And IIOT stands for Industrial Internet of things.
IoT sensor enables devices to exchange data with themselves via the internet.
This allows us to check and control the instrument parameters remotely. Which can get connected to smart devices like laptops, mobile phones, and so on.
For instance, you forgot to switch off your air conditioner at home while rushing to the office. After reaching your office, realize you need to turn off the AC.
Now here comes the IOT, which can get rid of you to go back home to switch off.
Rather you can do this with the comfort of your phone from the office. The same applies to industries, we check and control it remotely.

Types of IoT sensors:
There are many types of IOT sensors available in the market. One has to choose the sensor wisely based on the requirement. Below are the commonly used Industrial sensor types for understanding:
- Temperature Sensors
- Level Sensors
- Pressure Sensors
- Accelerometers
- Gyroscope
- Gas Sensors
- Infrared Sensors
Difference between normal sensors and IoT sensors:
In conventional sensors, the sensor can only collect data in an environment. Whereas IOT sensors integrate the connected devices locally. And link them with the real world via the internet.
Tips for implementing predictive maintenance:
1. Identify your critical equipment
2. Historical data analysis
3. Selection of sensors
4. Defining models and Machine learning algorithms
5. Understanding the early failures
6. Detecting outliers
7. Choose your best-suited software.
Disclaimer: The above-said points are only written for understand the basics of PdM, kindly take expert advice before implementing.
Maintenance in Instrumentation:
Instrumentation plays a vital role when it comes to maintenance and control. Because most of the equipment in industries relies on instrumentation. Which includes sensors, transmitters, valves, etc.,
In general, Instrumentation maintenance has the following checks:
- Physical Instrument Inspection
- Instrument Calibration
- Spare Instruments in stock
Physical Instrument Inspection:
Nowadays the above instrument maintenance has been replaced with ground surveillance robots. This reduces the manpower in the maintenance of large plants and offers great safety.
Instrument Calibration:
An important aspect of every instrument is calibration. This ensures the device is in good condition.
Here PdM gives accurate prediction and calibration due for each instrument. This involves analysis and comparison of historical calibration data.
For e.g.: If the error tolerance of an instrument is 0.01% and requires inspection every 3 months.
PdM will alert you even if there is any slight change in intolerance say 0.001% within 3 months. And gives a timely report on this.
This alerts the plant maintenance team to plan for calibration in advance.
Spare Instruments in stock:
To maintain good production, inventory management plays a vital role. Quick availability of parts and equipment ensures the smooth running of the plant.
This requires proper replenishment and stock maintenance. With the help of this, we can meet the above requirements.
Advantages of PdM in inventory:
- Easy track of items
- Prioritization of critical equipment
- Early assessment and replenishment alert
- Avoids unnecessary delay in the buying of items.
Maintenance in Industrial Automation:
Previously we have seen the field side maintenance. Now let’s overlook how it works on the system side which includes PLC, DCS, and SCADA.
The below architecture can help us to understand how it works.
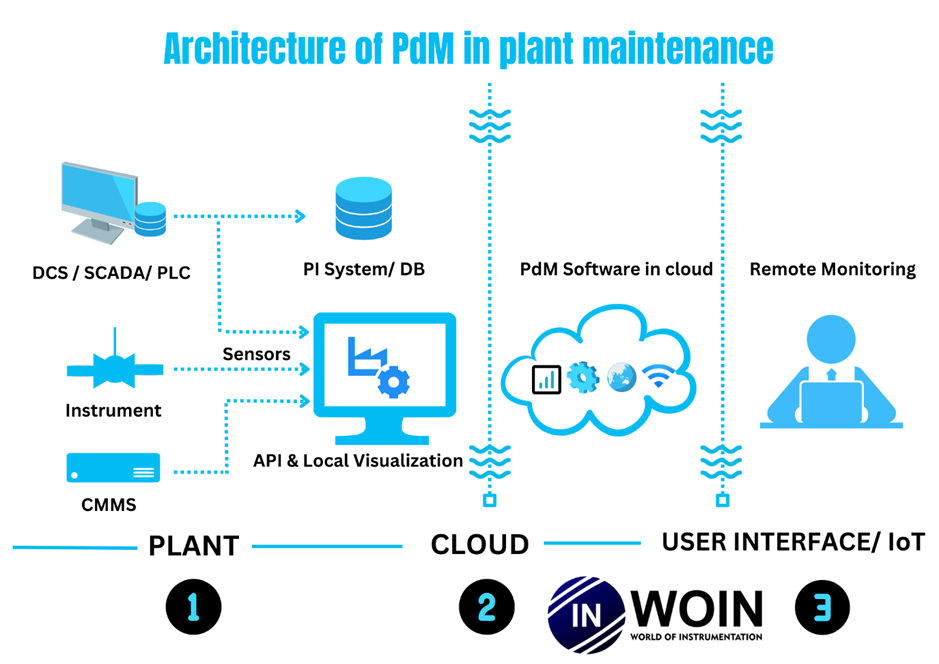
The PdM role here involves historical data collection and validation of controller assets. The scope of analysis can be set based on requirements.
PdM on the DCS involves historical data collection and validation of controller assets. The scope of analysis can be set based on requirements.
DCS system has many things to check and control from the hardware side to the software side.
Which requires many approved documents and reports for safety operations. Below are the advantages of PdM in Industrial Automation:
- Enables remote monitoring of the control system.
- Instant alert on critical equipment and common history.
- Quick system diagnostics and status from User Interface
- Integrates data of DCS environment with CMMS
- Saves time and money.
What is predictive maintenance (PdM) software?
It helps businesses to identify the performance of assets with its statistical process data analysis.
It especially saves time by providing reports, and schedules prior. This ensures safe operations and decreased downtimes.
Top 5 companies that provide predictive maintenance software:
1. Limble CMMS
2. Fracttal One
3. Flix
4. SAP Predictive Asset Insights
Courtesy: G2.com
Top 7 Predictive maintenance startup Companies in India:
Courtesy: f6s
Companies that offer predictive maintenance Services:
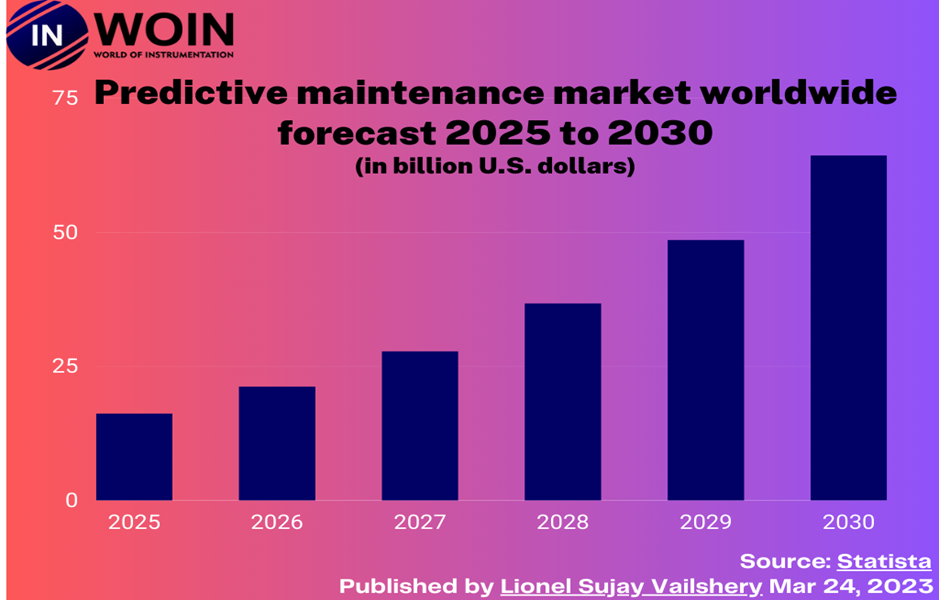
Predictive Maintenance Market Forecast:
Pros and Cons of predictive maintenance:
Pros:
- Early identification of equipment faults and breakdowns.
- Increase uptime from 10-15%
- It saves economically with fewer maintenance costs.
- Instant equipment reports and tracking.
- Avoids unnecessary downtimes.
- Improved safety functions and alerts.
- Offers early scheduled maintenance.
- Increases assets’ life.
- Overall, the above points improve product quality
Cons:
- Highly expensive
- Data collection takes more time.
- Sometimes it leads to false information.
- Needs more effective admin to understand complex algorithms.
Conclusion
“With Increased uptimes, decreased maintenance costs, and a safe environment”, IIOT predictive maintenance looks very promising for future industries.
– WOIN (World of instrumentation)
“A recent predictive maintenance report says the global PdM market can grow to 23B by 2025″.
So, it is important for industries to move towards digital solutions. Which predicts earlier asset failures and performs scheduled maintenance.
Thanks to AI-based predictive maintenance for this great transformation in the manufacturing sector.
Disclaimer
When first implementing predictive maintenance, start small. Use one or two critical assets on which to develop your predictive maintenance program.
Resist the urge to use too many sensors or to scale your predictive program too quickly. Allow the algorithm to stabilize while quantifying the projected returns on your investment.
Follow these steps, and with careful and systematic implementation, you can expect improved critical asset availability, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced revenues over time.
EndNote
I hope these resources and Knowledge will become helpful to you in the future. You can also give your input through the comment section.
And I continue to make this type of resource and knowledge-sharing posts on my website.
If you have any suggestions then feel free to ask in the comments and through email id, if you want to write an article on the website, please contact us by this mail id: contact@worldofinstrumentation.com
If you like this article, you can also like my previous article on Understand Repeatability and Reproducibility.
And you can also follow our LinkedIn group which is specially made for sharing information related to Industrial Automation and Instrumentation.
Author: Radha Krishnan Sivakumar
Author Profile: Click Here


![AdobeStock_289776099 [Converted]](https://worldofinstrumentation.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/AdobeStock_289776099-Converted-696x392.jpg)