Introduction: –
All listed questions are based on my own interview experience. So here are the Top Interview Questions on Instrumentation Part 1.
My goal is to make instrument engineers capable enough to get their field jobs.
In this move, I will try to give all the materials and references for getting your best job in the instrumentation field.
Top Interview Questions on Instrumentation Part-1
1. Define instrumentation.
Ans: –
Instrumentation is a combination of measuring instruments that indicate, measure, and record process variables in industries.
2. What is RTD? Explain.
Ans: –
RTD is a resistance temperature detector. It works on the principle of change in resistance due to temperature change.
It has a positive temperature coefficient which means when temperature increases the Value of resistance increases.
3. What are sensors and types of sensors?
Ans: –
A sensor is a device that takes physical input from the environment and converts it into a single device that humans or machines will interact with.
4. What is the difference between a Transducer, Sensor, Transmitter, And converter?
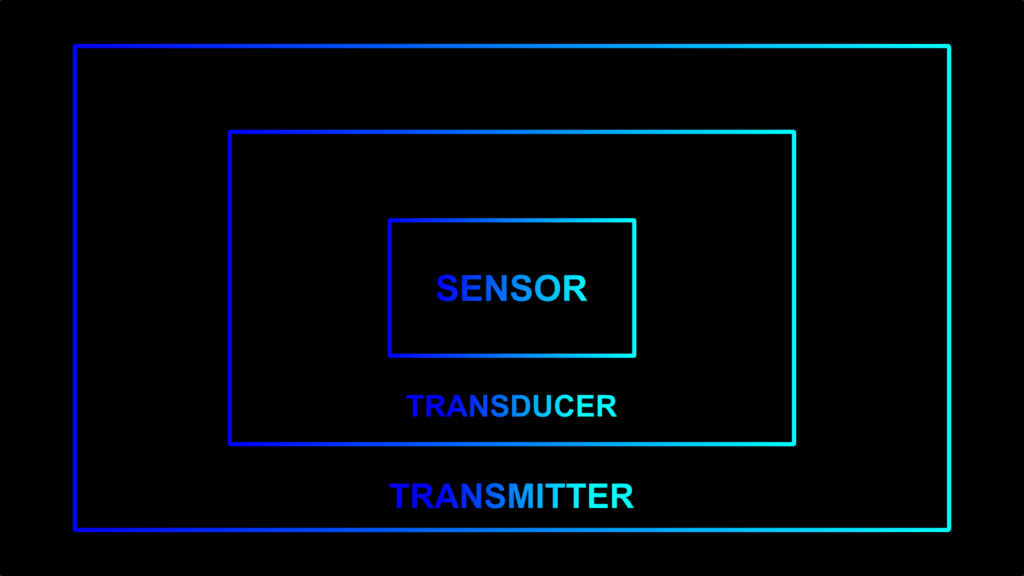
Ans: –
1. Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts one type of energy signal into another type of energy signal. Ex- LVDT is a transducer it converts mechanical movement into electrical output.
2. Sensor
A sensor is a device that takes physical input from the environment and converts it into a single one that humans or machines will interact with. Ex- Proximity sensor
3. Transmitter
A transmitter is a device that applies signal conditioning and scaling on the transducer signal and converts it into the industrial stranded signal.
Ex- temperature transmitter that converts thermocouple millivolt signal into 4-20mA signal
4. Converter
The converter is responsible for converting one type of industrial standard signal into another type of industrial standard signal.
The Ex- I/p converter converts a 4-20mA signal into a 3-15psi pressure signal.
5. What is the difference between a converter and a transmitter?
Ans: –
1. Transmitter
A transmitter is a device that applies signal conditioning and scaling on the transducer signal and converts it into the industrial stranded signal.
Ex- temperature transmitter that converts thermocouple millivolt signal into 4-20mA signal
2. Converter
The converter is responsible for converting one type of industrial standard signal into another type of industrial standard signal.
The Ex- I/p converter converts a 4-20mA signal into a 3-15psi pressure signal.
5. Why does the industry use a 4-20mA standard signal instead of 0-20mA?
Ans: –
In 0-20mA signal Controller does not distinguish between the Control signal or Cable break, when a 4-20mA signal is used instead of 0-20mA When the controller gets a 0mA signal then the controller easily finds out it is a wire Fault.
6. What is signal conditioning?
Ans: –
Signal conditioning is a process of manipulating an analog signal in such a way that the signal meets its requirement according to need.
7. Output of thermocouple?
Ans: –
The output of the thermocouple is in mV (Millivolt) on the principle of the see-back effect. The inverse effect of the see-beck effect is the Peltier effect.
8. Types of Level, Flow, Temperature, and Pressure Transmitter?
Ans: –
1. Level
- Capacitive type
- Ultrasonic type
- Radar type
- Radiation type
- Differential pressure type
2. Flow
- Magnetic type
- Vortex type
- Ultrasonic type
- venturi type
- Pitot type
- Orifice type
- Turbine type
- Coriolis mass flow type
- Thermal mass flow type
3. Temperature
- Thermocouple type
- RTD type
4. Pressure
- Differential pressure type
9. Types of orifice Plats?
Ans: –
- Concentric
- Eccentric
- Segmented
10. What is pt-100? Why is it called pt-100?
Ans: –
Pt 100 is a commonly used RTD. It is made of platinum and it has 100 ohms of resistance at 0*C
That’s why it is called pt-100.
11. What is absolute pressure?
Ans: –
Absolute pressure is the sum of gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure.
12. What are common flow transducers and their working principles?
Ans: –
1. Differential pressure
- Orifice meter
- Venturi meter
- Pitot tube
Above all, Bernoulli’s theorem of energy.
13. What is the valve coefficient?
Ans: –
The volume (in US gallons) of water at 60°F will flow per minute through a valve with a pressure drop of 1 psi across the valve.
14. What is the difference between 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire transmitters?
Ans: –
1. 2-wire
2- The wire transmitter has power and signal on the same line
2. 3-wire
in 3-wire combination power and signal connected to a separate line. but the ground is common between the source and panel.
4. 4-wire
In the four-wire configuration, the supply line and the signal line are fully isolated from each other. to reduce noise in the signal line.
15. Difference between thermocouple, RTD, and thermistor?
Ans: –
Thermistor: – Resistance changes with temperature but it is nonlinear. Used where high sensitivity is required.
RTD: – Resistance changes with temperature linearly. It has a positive temperature Coefficient.
Thermocouple: – It works on the principle of the Seeback effect. It gives output in Millivolts. It has a very high range so it is most commonly used in industry. Cold junction compensation.
16. Why is 3 to 15 psi used as standard instead of 0 to 15 psi?
Ans: –
It’s because below 3 psi is very low pressure which is hard to control or manipulate and also u have to provide a vacuum to allow for calibration and measurement hysteresis & repeatability errors.
17. Most common process parameters used in industry?
Ans: –
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Flow
- Level
- PH
18. What is a smart transmitter?
Ans: –
The smart transmitter is an advanced version of the transmitter. The smart transmitter has a microprocessor and it provides facilities like signal conditioning, environmental disturbance reduction, self-calibration, and self-diagnosing facilities.
19. What is the difference between Profibus PA and Profibus DP?
Ans: –
1) Profibus DP: – In Profibus-DP Protocol all I/O modules of PLC are transferred to the factory floor and using a single data cable all data will transfer to the plc.
2)Profibus-PA: – In Profibus PA all the factory floor instrument is connected to the signal bus cable and passed all single to segment coupler for converting the Profibus-PA signal into the Profibus DP signal.
20. What is the HART protocol?
Ans: –
The full form of the HART protocol is Highway Addressable Remote Transducer. It is a communication Protocol used for connecting transmitters to controllers.
It is a hybrid protocol. It means for communication it will use analog and digital signals on a single communication bus.
EndNote: –
Many of the interview questions come from your resume. It includes an area of interest you mentioned in your resume and your final year engineering project.
In this post, I will regularly update and give the latest information as possible so if you have any questions, please let me know in the comment section.



Please give answers for above questions …..
Yes!!
[…] Top Interview Questions for Instrument and control Engineers! […]
Good day! Would you mind if I share your blog with my zynga group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really appreciate your content.
Please let me know. Cheers